- +91 9511117684
- shweta@dataman.in

Table of Contents
Post Views: 4,246
Introduction: First Generation Doctor's Journey
Are you a first-generation doctor, or know someone who is ? This article is for first-generation doctors who want to start their practice. The article explores the real challenges faced by First generation Doctors in India and provides valuable insights to overcome them.
As a first-generation doctor, you may face unique challenges that others might not fully understand. Despite years of hard work, late nights, and sacrifices, you may still feel you are likely carrying student loan debt on your own and the pressure of building a stable future without family support. Balancing work and personal life can feel overwhelming, and it’s normal to wonder, “Do I really belong here?”or “Am I good enough?”Rest assured, these feelings are common, and you’re not alone. You’ve already achieved so much, but the question remains what’s next?
If you’re dreaming of starting a private practice but aren’t sure where to begin, I’m here to help you. I can guide you step-by-step, from planning your practice to ensuring its long-term success.
First Generation Doctor in India
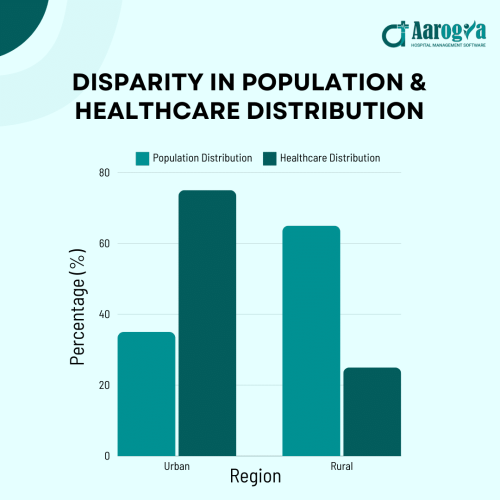
In India, the term “first-generation doctors” refers to individuals who are the first in their families to pursue and establish a career as a doctor. Traditionally, medical education has been a privilege of well-established, often wealthy families due to its high cost and intense competition. However, first-generation doctors are breaking these barriers and reshaping the landscape of healthcare. Their role becomes even more critical when considering a striking disparity as highlighted by PWC : 75% of doctors and healthcare infrastructure are concentrated in urban areas, while 65% of the population resides in rural regions. This urban-rural divide makes the emergence of first-generation doctors a vital step toward bridging the healthcare gap and ensuring equitable access for all.
Competition and Demand for Doctors in India
India Needs Doctors Like Never Before
India has only 60 doctors per 100,000 people, significantly below the World Health Organization’s recommended 100 per 100,000. PWC WHO
India’s population is growing, and so is the need for healthcare, especially with the rise in lifestyle diseases. As a first-generation doctor, you have unique opportunities to make a mark. Whether it’s exploring underserved areas, adopting telemedicine, or specializing in something you’re passionate about, the demand is there. It’s about finding your space and using your skills where they’re needed most.
Challenges Faced by First-Generation Doctors in India Solutions to overcome them
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Financial Constraints | High medical education costs leave new doctors at significant disadvantage to start off. |
| Lack of Guidance/Mentorship | Limited access to mentorship and guidance from experienced professionals. |
| Regulatory Compliance | First-generation doctors struggle with understanding complex regulatory requirements, lacking prior experience or guidance, leading to increased stress and time spent navigating compliance issues independently. |
| Limited Professional Network | Without family connections in the medical field first generations struggle to build Professional networks or find opportunities. |
“First Generation Doctors: Confused About Your Next Step?” Private Practice vs Job

Opening a healthcare-related business whether it’s a clinic, a diagnostic lab, a hospital, or a pharmacy or Pursuing a Job presents unique challenges that depend on factors such as capital investment, regulations, competition, and operational requirements. We are providing you a detailed comparative analysis of these challenges.
Starting Your Own Practice (Private Practice)
Challenges:
1. High Start-up Costs: Opening a practice involves significant upfront investment in office space, equipment, licensing, and staff.
Solution: Seek financial support through small business loans, grants, or partnerships with other doctors to share costs.
2. Administrative Burden: Running a practice can be challenging because it includes managing billing, insurance, compliance, and staff.
Solution: Invest in practice management software and hire a competent office manager to handle administrative tasks.
3. Risk and Uncertainty: A new practice may take time to become profitable, and there’s the risk of failure.
Solution: Develop a strong business plan, focus on marketing, and gradually build a loyal patient base to reduce financial risks.
Benefits:
- Greater earning potential as the owner
- Full control over your practice’s direction and patient care
- Flexibility in your schedule
1. Opening a Clinic
A medical clinic is typically the most accessible healthcare business for a first-generation doctor, but it still requires overcoming several barriers.
Challenges:
- Location: Selecting the right location for a clinic can be difficult. It must be accessible to the target patient and in an area with sufficient demand for the type of services offered.
- Competition: Clinics compete with other medical professionals, hospitals, and local health centers. The market may already be controlled by well-known doctors or large healthcare networks.
- Regulatory Compliance: Navigating local health regulations, obtaining licenses, and following medical practice laws can be a hurdle for newcomers.
- Cost: Initial costs may be lower compared to labs or hospitals, but still major especially for medical equipment, office space, and staff salaries.
Solutions:
Partnership : As a doctor you can partner with more experienced doctors in the fields that are directly related to you. For eg. As a pediatrician you can partner with a Gynecologist. Physiotherapists can partner up with Orthopedic surgeons.
Symbiotic relation of doctors :
1. Cardiologist and Endocrinologist
Diabetes prevalence is expected to reach 73.5 million cases by 2025 according to PWC highlights the growing burden of chronic diseases and the increasing demand for endocrinologists and related specialists.
2. Oncologist and Radiologist
Based on a McKinsey report on healthcare strategies, the demand for specialists like cardiologists and oncologists is expected to rise by 40% due to the growing prevalence of non-communicable diseases (NCDs).
3. Dermatologist and Plastic Surgeon
Dermatologists treat skin conditions and plastic surgeons perform surgeries to improve appearance.Together they provide complete care for skin,health and aesthetics.
4. Nephrologist and Urologist
Nephrologists focus on kidney health, while urologists address urinary tract conditions. They collaborate to treat complex issues like kidney stones and urinary tract issues.
5. Psychiatrist and Psychologist
- Location Selection: Choosing the right location for a clinic is crucial for the success of any healthcare practice, Choose location with High Foot Traffic, Affordable Rent, Proximity to Residential Areas, Near Hospitals or Medical Centers
(1.) Understand Local Regulations
Research specific licenses, permits, and certifications required.
Certifications and Accreditations required to open a Clinic in India
| License Name | Why It’s Important | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Clinic Registration Certificate | Ensures legal standards for safety and quality. | A general healthcare clinic in Bengaluru. |
| Doctor’s License | Legally allows doctors to treat patients. | An ENT specialist registered with the Medical Council of India. |
| Trade License | Permits a clinic to operate as a business. | Private clinic operating in Delhi. |
(2.) Seek Legal and Professional Advice
- Hire a healthcare lawyer or consultant to help navigate legal requirements.
- Consult with experienced clinic owners or mentors to understand common pitfalls.
(3.) Use Compliance Software
Investing in healthcare-compliant software, like Aarogya DM Aarogya, is vital for efficiently managing documentation, audits, and deadlines, especially when opening a clinic in India. With the introduction of the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission ABDM digital integration has become central to modern healthcare management. Such software ensures compliance with ABDM guidelines, streamlining patient recordkeeping, telemedicine, and coordination with the national healthcare system.
2. Opening a Lab (Diagnostic Centre)
A diagnostic lab requires specialized medical knowledge, equipment, and adherence to regulatory standards, making it more complex than opening a clinic.
Challenges:
- High Initial Investment: Diagnostic equipment (such as MRI, X-ray machines, blood analysers, etc) are very costly. Renting or purchasing the required space is also expensive.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Labs are subjected to strict regulations, including accreditation (e.g., NABL in India) and compliance with health standards.
- Staffing: Labs require specialized staff, including technicians and qualified lab professionals. Recruiting skilled personnel can be challenging, particularly in areas with a shortage of qualified workers.
Solutions:
Certifications and Accreditations required to open Laboratory in India
| Certification/Accreditation | Purpose |
|---|---|
| FSSAI License | Ensures compliance with food safety and laboratory hygiene standards. |
| Drugs License (for handling diagnostic reagents) | Required for the sale and distribution of diagnostic reagents and chemicals. |
| Biomedical Waste Management Authorization | Ensures proper handling, disposal, and management of biomedical waste. |
- Implement Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Develop clear SOPs for testing, safety, and waste management to maintain compliance and quality.
- Maintenance Contracts: Sign maintenance contracts with equipment providers to ensure timely repairs and updates.
- Adopt Laboratory Management Software: Use software to streamline operations, manage test results, and reduce human errors.
3. Opening a hospital
Opening a hospital is one of the toughest tasks in healthcare. It requires extensive planning, large-scale financing, and considerable administrative expertise.
Challenges:
- Capital Investment: The costs of land, construction, medical equipment, and facilities are extremely high. The required investment for starting a hospital often runs into millions of dollars.
- Regulatory Approvals: Hospitals are subject to a wide range of regulations, including safety codes, staffing requirements, and accreditation standards (e.g. JCI). Obtaining the necessary licenses can take a long time.
- Staffing: Recruiting a wide range of medical professionals (doctors, nurses, administrative staff, etc.) and ensuring they meet quality standards is a challenge, especially in competitive healthcare markets.
Solutions:
Navigating Regulatory Compliance
Obtain Necessary Certifications and Accreditations:
Certifications and Accreditations required to open a hospital in India
| Certification/Accreditation | Purpose |
|---|---|
| NABH Accreditation | Ensures high standards of patient care, safety, and management. |
| Clinical Establishment Registration | Legally registers the hospital under the Clinical Establishments Act. |
| ISO Certification | Demonstrates adherence to quality management systems and standards. |
Ongoing Staff Training: Continuous staff training on compliance, patient care, safety, and regulations with nursing agencies involvement.
Securing Funding and Managing High Initial Costs: Explore government healthcare grants, loans, and partner with TPAs for infrastructure and hospital development.
Hospital Management Software: Utilize Hospital Management Software to streamline operations, supporting first-generation doctors in building efficient hospitals.
4. Opening a Pharmacy
Opening a pharmacy can be a profitable business with lower start-up costs compared to clinics, labs, or hospitals. However, pharmacies still face several important challenges.
Challenges: Regulatory Compliance
- Financial and Funding Challenges: Opening a pharmacy requires substantial upfront investment in inventory, equipment, and licensing. First-generation doctors may struggle to secure funding or have limited access to financial networks
- Building a Customer Base and Reputation: As a first-generation doctor opening a pharmacy, you may not have a built-in customer base, making it difficult to attract patients and establish trust in a competitive market.
Solutions:1. Regulatory Compliance
Licenses required to open a pharmacy in India
| License Name | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Drug License | Permits the sale, storage, and distribution of medicines legally. |
| GST Registration | Ensures compliance with tax regulations and facilitates proper billing |
| Trade License | Allows the business to operate legally and safely. |
- Train Your Team: Make sure your staff understands and follows laws about medication safety and patient privacy.
- Use Software: Invest in pharmacy software that helps you manage prescriptions and keep track of inventory while staying compliant with laws.
Simplify managing prescriptions, tracking inventory, and staying compliant with Aarogya’s Pharmacy Software DM Aarogya
2. Financial and Funding Challenges
- Look for Loans or Grants: Search for government loans or grants that can help you start your pharmacy.
- Partner Up: Consider teaming up with other businesses or suppliers to share costs and reduce risks.
3. Building a Customer Base and Reputation
- Get Involved Locally: Attend community events, offer free health checks, or talk to people in the area to let them know about your pharmacy.
- Your brand in OPD decides your Pharmacy.
- Offer Great Service: Provide excellent customer service, like delivering medications or offering advice, so customers trust you and keep coming back.
- Use Online Marketing: Integrate with ONDC to expand your pharmacy’s reach and connect with a wider audience across multiple platforms.
Pursuing a Job (Working for a Hospital or Clinic)
Challenges:
1. Limited Autonomy: Working for an employer means you are following the organization’s policies and procedures, which can limit your decision-making power.
Solution: Focus on roles that allow for some level of leadership or influence, such as department head or supervisor positions.
2. Lower Earning Potential: Salaries are often fixed, which may not offer the same growth potential as owning a practice.
Solution: Look for opportunities to work in high-demand specialties or in regions with physician shortages to maximize income.
3. Enhancing Medical Practice Through Mentorship: Doctors get limited hands-on Practice/ Direct Interactions with the patients since the Reputed Organisations have their own set of Doctors/HODs and protocols in place. So the medical practice of the Doctor has a slower learning curve.
Solution : Maintain a student mentor relationship with the HODs and higher level doctor authorities.
Benefits:
- Job security with a steady income
- Less financial risk
- Opportunity for professional development and mentorship.
Which Option is Best for you?
Ultimately, the choice depends on individual preferences, financial situation, and long-term goals. Here’s a quick breakdown: Pursuing a Job may be ideal if you prefer job security, a structured environment, and fixed income, especially if you’re new to the medical field or if you want to focus on patient care without the burden of running a business. Starting Your Own Practice could be the best choice if you’re entrepreneurial, have a passion for independence, and are willing to take on the financial and administrative challenges in exchange for higher earning potential and more control over your work life. As a first generation doctor, starting with a job might be a safer option to build experience, financial stability, and confidence before entering into private practice. However, if you have the sufficient resources and budget, your own practice could be a fulfilling long-term goal.
FAQ’S
1. What are the biggest challenges faced by first-generation doctors?
First-generation doctors often face unique challenges such as financial constraints, regulatory compliance, limited business knowledge, building patient trust, attracting skilled staff, managing operations, and balancing clinical and business responsibilities.
2. How can first-generation doctors overcome financial barriers when starting their practice?
To overcome financial barriers, first-generation doctors can explore options such as small business loans, grants, and government programs. Additionally, partnering with other doctors, seeking financial advisors, and leveraging practice management software to reduce overhead costs can be helpful.
References
You can also refer
- Times of India
- National Medical Commission (NMC): Offers insights into policies and systemic barriers in Indian medical education. Visit NMC
- Public Health Foundation of India (PHFI): Discusses access, equity, and challenges in healthcare education. Visit PHFI
- AIIMS Research Publications: Highlights challenges in medical education and systemic gaps for underrepresented students. Visit AIIMS
- National Informatics Centre (NIC): Features government policies addressing challenges in medical education. Visit MoHFW
- Educational Research by NCERT: Examines barriers faced by first-generation learners in professional fields. You can explore their publications section for related studies or contact them directly through their official site: NCERT
0

