- +91 9511117684
- shweta@dataman.in
How Medicines Are Made: Inside Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Process

Table of Contents
Post Views: 7,567
Introduction
How Medicines Are Made: Ever wondered how the tiny pill you take for a headache or the syrup your doctor prescribes is actually made? Medicine production, or pharmaceutical manufacturing, is a meticulous journey that begins with an idea and ends with a life-saving product on the shelf.
In this blog, we break down how medicine is made, what regulations govern its development, and how modern solutions like pharmacy production software are transforming pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Tools like Dm Aarogya are streamlining production with automation and compliance-ready modules, helping ensure efficiency and regulatory adherence in every step of the process.

1. What is Medicine Production?
Medicine production is the science of creating pharmaceutical products in a controlled and regulated environment. Pharmaceutical manufacturing involves the industrial-scale synthesis of pharmaceutical drugs. This process is meticulously designed to ensure that medications meet stringent quality standards, ensuring their safety and efficacy.
The production process can be broadly categorized into:
- Primary Processing: Converting raw materials into active ingredients.
- Secondary Processing: Turning these active ingredients into tablets, syrups, or injectables.
This process must comply with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) laid out by global and national authorities like the FDA, WHO, and CDSCO.
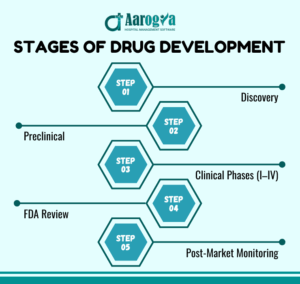
2. From Molecule to Market: Stages of Drug Development
1. Drug Discovery & Preclinical Research
In this phase, scientists study potential drug compounds to see if they can provide therapeutic benefits.
Preclinical testing involves lab experiments and animal testing to check the safety and effectiveness of these compounds before human trials.
2. Preclinical Research:
During preclinical research, compounds are tested in the lab and on animals to ensure they are safe and effective. This step helps determine if the compound is ready for human testing.
3. Clinical Research:
Human trials are conducted in multiple phases to evaluate the drug’s safety and efficacy.
These are typically conducted in four phases:
Phase I – Tests safety in a small group.
Phase II – Evaluates efficacy and side effects.
Phase III – Large-scale testing on diverse populations.
Phase IV – Post-market surveillance
4. FDA Review:
Comprehensive evaluation by regulatory bodies like FDA determines whether the drug can be approved for public use.
5. Post-Market Safety Monitoring:
Ongoing surveillance ensures that any long-term or rare side effects are identified and addressed.
Each phase is critical to ensure that only safe and effective medications reach the market.
Read more on The Pharmaceutical Journal
3. The Manufacturing Process: Step-by-Step
Transforming active pharmaceutical ingredients into final drug products involves several precise steps:
A. Formulation
Active ingredients are combined with excipients to create a stable and effective product. This step ensures that the medication delivers the intended therapeutic effect consistently.
B. Mixing and Granulation
The blended materials are mixed thoroughly, and granulation may be performed to improve the flow and compression characteristics of powders.
C. Drying
The granulated mixture is dried to achieve the desired moisture content, which is crucial for the stability and compressibility of the final product.
D. Compression and Encapsulation
The dried granules are compressed into tablets or filled into capsules, forming the final dosage forms.
E. Coating
Tablets may be coated to protect the drug substance, mask taste, or control the release of the medication in the body.
F. Packaging and Labeling
The final products are packaged in suitable containers and labeled with essential information, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards and providing critical information to healthcare providers and patients.
Each step is governed by strict protocols to maintain the highest quality standards.
4. Quality Control and Regulatory Approvals
Strict regulatory frameworks govern pharmaceutical production. In India, compliance with GMP standards by CDSCO and the Drugs and Cosmetics Act is mandatory. Globally, the FDA , TGA (Australia), and EMA (Europe) supervise approvals.
Ensuring the safety and efficacy of pharmaceutical products is paramount. Regulatory agencies enforce CGMP to oversee manufacturing processes. Compliance with CGMP assures that drugs meet quality standards and are consistently produced and controlled.
More on how US FDA Evaluates and Ensures Compliance:
CDSCO Guidelines
- FDA Manufacturing Compliance
- TGA Manufacturing Info
Quality Control and GMP Standards
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) form the backbone of the pharmaceutical world. GMP ensures that products are consistently produced and controlled according to quality standards.
Major QC Measures:
- Batch-wise testing
- In-process checks
- Final product inspection
- Storage and expiry compliance
Regulators perform random audits, and digital systems often log each batch activity, reducing the risk of manual error. FDA GMP Compliance
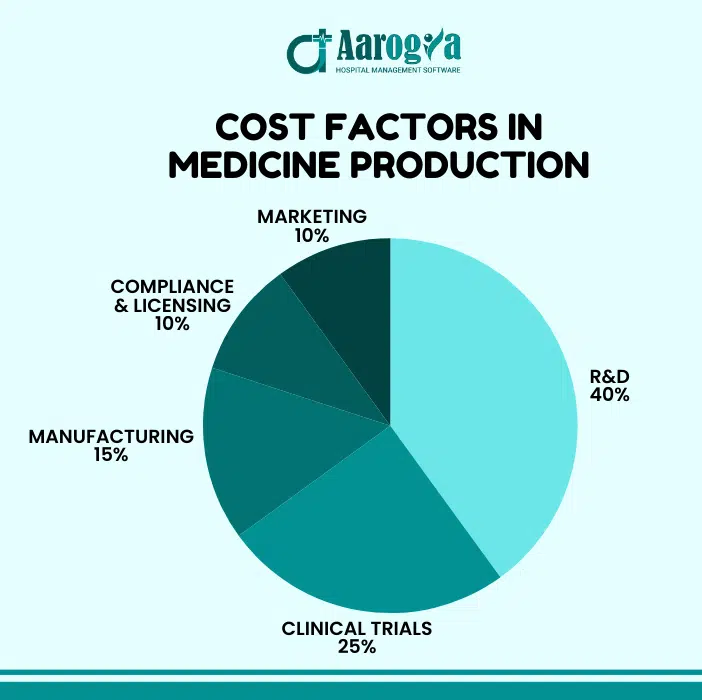
5. Cost Factors in Medicine Production
Developing and manufacturing pharmaceuticals is a resource-intensive endeavor influenced by various factors:
Cost Factor | Impact |
R&D | Billions in investment over years |
Clinical Trials | Human testing and documentation |
Facility Setup | Equipment, quality control labs |
Marketing & Distribution | Education, supply chain logistics |
- Research and Development (R&D): Significant investment is required to discover and develop new drugs, often involving years of research and substantial financial resources.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meeting stringent regulatory standards necessitates continuous monitoring and adaptation, incurring additional costs.
- Manufacturing Processes: Implementing advanced technologies and maintaining high-quality standards contribute to production expenses.
- Market Dynamics: Pricing strategies must balance affordability for patients and recouping investment costs, influenced by market competition and healthcare policies.
Understanding these factors is crucial for developing strategies to manage costs without compromising on quality. CRSToday
6. Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Processes
Pharmaceutical manufacturing involves several processes to produce active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and formulate them into final products.
Chemical Synthesis
Chemical synthesis involves creating complex compounds from simpler substances. It’s fundamental for producing APIs, ensuring scalability, consistency, and cost efficiency. The process includes:
- Route Selection: Choosing the most efficient synthesis pathway.
- Feasibility Studies: Assessing scalability and practicality.
- Optimization: Refining reaction conditions for maximum yield and purity.
Fermentation
Fermentation uses microorganisms to produce compounds like antibiotics and vaccines. Steps include:
- Culturing: Growing microorganisms under controlled conditions.
- Scaling-Up: Expanding cultures to production volumes.
- Fermentation Process: Microorganisms convert substrates into desired products.
- Downstream Processing: Purifying and formulating the product.
This method is essential for producing complex biological products.
Bioprocessing
Bioprocessing utilizes living cells to produce therapeutic products, including monoclonal antibodies and gene therapies. It involves:
- Cell Line Development: Selecting and optimizing cells for production.
- Upstream Processing: Culturing cells and facilitating product expression.
- Downstream Processing: Harvesting, purifying, and formulating the final product.
Bioprocessing is at the forefront of developing advanced therapies.
7. Software Solutions in Pharmaceutical Production
Incorporating advanced software solutions has become essential in modern pharmaceutical manufacturing. These systems offer:
- Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES): Monitor and control production processes, ensuring efficiency and compliance.
- Quality Management Systems (QMS): Facilitate adherence to quality standards and streamline documentation.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): Integrate various business processes, enhancing coordination and decision-making.
Implementing these technologies leads to improved productivity, reduced errors, and enhanced regulatory compliance. ISPE
Future of Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
The industry is moving towards personalized medicine, AI-led formulations, and automated production.
Key Future Trends:
- 3D printing of tablets
- Smart drug packaging
- Real-time release testing
- Continuous manufacturing instead of batch-based
This future demands systems that go beyond manual registers capable of handling production templates, tracking SKUs, and auto-calculating sale and MRP rates for pharmacy-level data.
8. Tech Integration in Pharmaceutical Production
Modern pharmaceutical facilities are turning to smart manufacturing systems that ensure accuracy and compliance.
Smart Features Include:
- Batch production registers
- Auto-calculated stock and pricing
- FIFO stock tracking
- Regulatory template-based formulations
- Real-time dashboard alerts for compliance deviations
Several leading software platforms dmAarogya offer tailored solutions for pharmaceutical production units designed to reduce wastage, speed up formulation, and maintain audit-ready logs.
These tools are silently transforming how medicines are made, helping companies stay competitive and regulatory compliant.
Conclusion
Medicine production is far more than a factory process; it’s the heartbeat of global healthcare. Every capsule, syrup, or injectable is the result of years of research, strict regulatory checks, and meticulous production protocols. With rising demands for quality, speed, and transparency, pharmaceutical manufacturers must embrace smart technologies, automation, and compliance-driven software to stay ahead.
Adopting advanced solutions like dmAarogya in your production process can ensure minimal wastage, real-time quality tracking, regulatory readiness, and cost-effective operations.
Remember, efficient medicine production saves time, money and most importantly, lives.
Also Read: How to Open a Clinic in India: A Doctor’s Step-by-Step Guide
FAQ’s
1. What are the basic raw materials used in medicine production?
APIs (Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients), excipients (binders, preservatives, etc.), solvents, and packaging materials like blister foils or bottles.
2. What is the difference between API and formulation in pharma?
API is the core active compound that treats the condition, while formulation includes the API + excipients to create the final drug product.
3. How is medicine quality tested before release?
Through analytical lab tests, stability studies, microbial analysis, dissolution profiling, and final batch quality checks as per pharmacopeia standards.
4. Is automation common in pharmaceutical manufacturing?
Yes. Automation improves accuracy, reduces human error, and ensures traceability from raw material intake to final packaging.
5. Can digital software help with regulatory audits?
Absolutely. Software tools maintain audit trails, batch logs, compliance checklists, and auto-generate reports aligned with CDSCO, WHO-GMP, and FDA guidelines.
6. How is medicine tracked after production?
Through barcoding, serialization, and integrated software that enables real-time inventory tracking and counterfeit prevention.
0