Best Apparel Manufacturing Software for Your Business
Apparel and textile industry is one of the largest industries in the world. In India, it contributes around 2.3% of the country’s GDP and around 10.5% of the country’s export earnings.
The industry is highly diversified and apparel manufacturing is one of the most sought after and challenging segments. Some of the major challenges are high labour cost, increasing competition and sustainability concerns.
To overshadow the competition and thrive in industry, apparel manufacturing companies must adopt technologies that streamlines production, improves efficiency, and provides real-time data for informed decision-making.
This is where the role of Apparel Manufacturing Software comes in. By automating various aspects of the production process, this software can significantly reduce errors, optimize resource allocation, and enhance overall productivity.
In the blog, we will discuss the best apparel manufacturing software and how to choose the right apparel manufacturing software for your business.
Read More: What is a Queue Management System and Why Do You Need One?
What is Apparel Manufacturing Software?
Apparel manufacturing software is a specialized ERP solution designed to streamline and optimize the operations of apparel manufacturing businesses. The software encompasses a wide range of features to support businesses at every stage of the value chain.
The software solution is essential for modern businesses due to the numerous challenges they face. By leveraging this software solution, companies can:
- Streamline processes and improve efficiency to faster production times.
- Optimize inventory management to minimize material waste and reduce costs.
- Create a more organized and streamlined workflow.
- Access real-time data and analytics to make informed decisions about production planning, resource allocation, and cost management.
- Gain a competitive edge and improve operational efficiency.
Key Features to Look for in the Best Apparel Manufacturing Software
An efficient apparel manufacturing software should have following features:
Process Management
Process management helps you efficiently manage your entire production process, from order placement to shipment. Further, it helps in streamlining workflows, reducing bottlenecks, and ensuring timely delivery.
Inventory Management
Inventory management is a complex process, if you are doing it manually. With the help of apparel manufacturing software you can maintain accurate inventory records, track stock levels, and prevent overstocking or shortages.
Cost Management
See exactly how much your products cost to make, find ways to save money, and use data to make smart business choices. Keep track of your spending, set budgets, and make your business more profitable.
Reporting and Analytics
Create detailed reports and analyze important numbers (KPIs) to track how your business is doing. Use the latest information to make smart choices and spot patterns.
Supply Chain Management
Work together effortlessly with your suppliers and business partners to make sure your products get from point A to point B without a hitch. Keep track of how your vendors are doing, watch your shipments closely, and find the best ways to move things around efficiently.
Financials
Take care of your money matters smoothly. This includes keeping track of your income and expenses, sending out bills, and handling payments. Make sure your financial records are accurate and follow all the rules.
Stock Management
Keep a close eye on your inventory, know exactly what products you have and how many, and make sure you’re selling them quickly. Avoid running out of stock, and keep costs down by not holding onto too much inventory.
Sales/Purchase Management
Make your sales and buying easier! From placing orders to getting them delivered, our software will simplify everything. Build strong relationships with your customers, keep track of how much you’re selling, and get the best deals from your suppliers.
Billing Management
Simplify your billing process by automating it. Generate accurate invoices quickly and easily, and keep track of payments. This will help you improve your cash flow and make fewer mistakes.
Quality Control
Make sure your products are top-notch! Set up a system to check the quality of everything you make, so it’s perfect for your customers. If you find any problems, fix them quickly to avoid wasting time and money.
Integration with Other Systems
Easily link your apparel manufacturing software to other tools like ERP, CRM, and online stores. This will make it easier to share information, work faster, and get a complete picture of your business.
Read More: Understanding IPD vs OPD | Difference Between IPD and OPD
Benefits of Implementing Apparel Manufacturing Software
1. Increased Efficiency and Productivity
One of the most immediate benefits of using apparel manufacturing software is the significant increase in efficiency and productivity. The software automates routine tasks like data entry, inventory management, and order processing, allowing your team to concentrate on more strategic and valuable work. This efficiency boost results in faster turnaround times, fewer bottlenecks, and a smoother overall workflow.
2. Real-Time Data and Insights
The software gives you a central place to keep track of how your products are being made, how much inventory you have, and how well your business is doing. This data can help you find ways to improve your business, use your resources more efficiently, and make changes that will help your business grow.
3. Cost Savings
By automating processes and providing accurate demand forecasting, it helps you avoid overproduction and reduce excess inventory. This means less wasted materials and lower storage costs.
Furthermore, the integration of software with supply chain management systems ensures efficient procurement, minimizing the risk of material shortages. This reduces downtime and prevents delays in production.
4. Scalability
Whether you’re a small-scale manufacturer or a large-scale enterprise, the apparel manufacturing software is designed to grow with your business. The software’s flexible structure lets you tailor its features to fit your exact needs, no matter how big or small your business is. As your company expands, the software can easily adjust to handle more products, larger production runs, and changing business demands.
5. Enhanced Product Quality
Maintaining consistent product quality is crucial to the success of any apparel manufacturing business. A reliable apparel management software can significantly support your quality control efforts.
By providing tools to track production standards, document inspection results, and identify potential defects early in the process, this software helps you proactively ensure that your products meet or exceed customer expectations. This not only enhances your brand reputation but also drives customer satisfaction.
Vastralaya: Best Apparel Manufacturing Software
Vastralaya is a custom-built apparel manufacturing software designed to meet the unique needs of the industry. With its user-friendly interface, powerful features, and scalability, Vastralaya empowers businesses to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and drive growth.
Why Choose Vastralaya?
- Customization: Vastralaya can be customized as per the requirements of your business.
- Seamless Integration: Our software seamlessly integrates with your existing systems, ensuring a smooth workflow and minimizing data entry errors.
- Advanced Features: Our apparel manufacturing software boasts advanced features such as process optimization, real-time inventory tracking, and intelligent cost management.
- User-Friendly Interface: Vastralaya is easy to learn and use, even for those with limited technical experience.
- Scalability: Vastralaya is capable enough to meet your growing requirements.
- Tailored for the Apparel Industry: Vastralaya is specifically designed to meet the unique requirements of apparel manufacturers.
- Expert Support: Our dedicated support team is always available to assist you with issues you may encounter.
Read More: What is POS Software and How Does It Work
Conclusion
The selection of right apparel manufacturing software is essential for businesses to thrive in this competitive industry. It’s crucial to consider factors such as scalability, customization options, integration capabilities and other key features in the solution you are looking for.
Vastralaya emerges as a clear leader in the market, offering a comprehensive suite of features designed to meet the unique needs of apparel manufacturers.
Schedule a free demo of Vastralaya today and discover how our software can help you achieve your business goals.
On-Premise Vs. Cloud Based POS System: Which is Right for Your Business?
Point-of-sale (POS) systems have become indispensable tools for businesses of all sizes, streamlining operations and providing valuable insights into customer behavior. These systems, which are typically comprised of hardware and software components, enable businesses to process transactions, manage inventory, and track sales data.
When considering a POS system, businesses are often faced with a crucial decision that is whether to opt for an on-premise or cloud-based POS system solution. While both options have their advantages, cloud-based POS systems have emerged as a compelling choice for many businesses due to their inherent flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness.
Read More: What is POS Software and How Does It Work
On-Premise POS Systems
On-premise POS systems are software solutions that are installed and operated on a local server. These servers are the business’s own hardware. This typically involves purchasing servers, workstations, and other necessary equipment to run the POS application on the business’s premises.
Key characteristics of on-premise POS systems include:
- Physical hardware: Requires on-site equipment for installation and operation.
- Local control: Businesses have complete control over the system’s hardware and software.
- Internal IT management: Requires in-house IT resources for maintenance and updates.
Advantages of On-Premise POS Systems
- Control: Businesses have full control over their POS system, including data storage, customization, and security.
- Customization: On-premise systems can be tailored to specific business needs and workflows.
- Security: Businesses may feel more secure knowing their data is stored on their own premises.
Potential Drawbacks of On-Premise POS Systems
- Upfront costs: On-premise systems often require a significant upfront investment in hardware and software.
- Maintenance: Businesses need to allocate resources for ongoing maintenance, updates, and troubleshooting.
Scalability: Scaling an on-premise system can be challenging and expensive, especially as a business grows.
Cloud-Based POS Systems
Cloud-based POS systems, also known as cloud POS or Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) POS, are hosted on remote servers accessible via the internet. Unlike on-premise systems, which require physical hardware and software installation, cloud POS solutions are delivered as a service, eliminating the need for significant upfront investments.
As per a report, Cloud-based HMS is gaining popularity due to its scalability, cost-effectiveness, and ease of access.
Advantages of Cloud-Based POS Systems
- Accessibility: Cloud-based POS systems can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, providing flexibility and convenience for businesses with multiple locations or remote employees.
- Scalability: Cloud POS solutions can easily adapt to changing business needs. As your business grows or shrinks, you can adjust your subscription plan accordingly, ensuring optimal resource allocation.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Cloud-based POS systems often have lower upfront costs compared to on-premise systems. Additionally, subscription-based pricing models eliminate the need for ongoing maintenance expenses.
- Regular Updates: Cloud providers automatically update the software, ensuring that businesses always have access to the latest features and security patches.
- Disaster Recovery: Cloud-based systems typically include built-in disaster recovery features, safeguarding your data in case of hardware failures or natural disasters.
Addressing Common Concerns
- Data Security: While data security is a valid concern, reputable cloud providers implement robust measures to protect sensitive information. These measures often include encryption, access controls, and regular audits.
- Internet Connectivity: Reliance on a stable internet connection is a potential drawback. However, with the increasing availability and reliability of broadband internet, this concern is becoming less significant for many businesses.
- Vendor Lock-in: Some businesses may worry about becoming dependent on a specific cloud provider. It’s essential to choose a provider with a flexible contract and a reputation for customer satisfaction.
Read More: What is Cloud Kitchen? A Guide for Restaurant Owners
On-Premise Vs. Cloud Based POS System
| Feature | On-Premise POS System | Cloud Based POS System |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | Higher | Lower |
| Ongoing Costs | Maintenance, upgrades, IT support | Subscription fees |
| Scalability | May require hardware upgrades | Easily scalable |
| Control | More control over hardware and software | Less control, but often managed services |
| Accessibility | Limited to on-site access | Accessible from anywhere with an internet connection |
Data Security | Depends on in-house security measures | Relies on vendor’s security measures |
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing
When deciding between an on-premise or cloud-based POS system, several key factors should be carefully evaluated to ensure the best fit for your business.
Business Size and Needs: The scale of your operations and specific requirements will significantly influence your choice. Small businesses may find a cloud-based POS system more suitable due to its lower upfront costs and scalability. Larger enterprises with complex needs might benefit from an on-premise solution for greater control and customization.
Budget: Consider the initial investment and ongoing costs associated with each option. On-premise systems often require a substantial upfront expenditure for hardware, software, and installation. Cloud-based systems, on the other hand, typically have lower upfront costs but may incur recurring subscription fees. Evaluate your budget constraints and long-term financial goals to determine the most cost-effective choice.
Technical Expertise: Assess your team’s capabilities for managing IT infrastructure. On-premise systems require in-house technical expertise for installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting. Cloud-based systems, however, are generally easier to manage as the provider handles most technical aspects. Consider the availability of internal resources or the need for external IT support to determine the most suitable option.
Data Security: Data security is a critical concern for businesses of all sizes. Both on-premise and cloud-based systems can be secure when implemented correctly. However, cloud-based providers often have dedicated security teams and advanced infrastructure to protect sensitive data. Research the security measures in place for your chosen provider to ensure your data is adequately protected.
Scalability: Consider your business’s growth potential and the ability of the system to adapt. Cloud-based POS systems are highly scalable, allowing you to easily add or remove features and users as your business expands. On-premise systems may require more significant hardware and software upgrades to accommodate growth. Evaluate your future plans and choose a system that can support your business’s evolving needs.
Read More: Impact of GST on Hotel Industry
Aatithya POS Software
Aatithya offers a state-of-the-art Point of Sale (POS) software designed to streamline operations and enhance customer experiences. Our solution is tailored to meet the diverse needs of businesses, from small retail stores to large-scale enterprises.
Key Features and Benefits:
- Intuitive Interface: Our user-friendly interface ensures easy navigation and efficient workflow.
- Robust Inventory Management: Track stock levels, manage purchase orders, and prevent stockouts.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Build strong relationships with customers and personalize their shopping experience.
- Payment Processing: Accept various payment methods, including credit cards, cash, and digital wallets.
- Reporting and Analytics: Gain valuable insights into your business performance with detailed reports.
Read More: Night Audit: Steps in Night Audit process in Front Office
Conclusion
In conclusion, the choice between an on-premise and cloud-based POS system ultimately depends on the specific needs and circumstances of your business. While on-premise systems offer greater control and customization, cloud-based POS systems often provide more flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness.
If you’re considering a POS system for your business, we encourage you to contact our team of experts to discuss your specific requirements. We can help you evaluate your options and determine which solution is the best fit for your organization.
Which is Best Steel for Construction in India
Steel, the backbone of modern construction, is more than just a building material; it’s the foundation upon which entire cities are built. Its strength, durability, and versatility have made it an indispensable component of the construction industry for centuries.
The construction industry is the largest consumer of steel, accounting for approximately 50% of global steel production each year.
With the Indian construction sector booming, selecting the best steel for construction in India is essential for real estate developers.
This blog will explore the top 5 best steel options for construction in India, each playing a vital role in the building process.
Read More: Top 5 Best Cement in India with Latest Cement Bag Prices
Which Steel is Best for Construction?
When selecting the best steel type for construction, TMT (Thermo Mechanically Treated) bars are often the preferred choice. They are particularly popular for residential construction.
TMT bars are graded as Fe415, Fe500, Fe500D, and Fe550. Higher grades of steel are also available for construction.
TMT Steel is a thermo-mechanically treated steel bar, produced using the TEMPCORE technology.
TMT bars are known for their strength, ductility, and durability, ensuring safe and long-lasting building structures. Their distinctive manufacturing process results in high yield strength, making them especially well-suited for high-rise buildings and homes located in seismic or earthquake-prone regions.
Factors to Consider Before Buying TMT Bars for Construction
When purchasing TMT (Thermo Mechanically Treated) bars for your house construction project, it’s essential to ensure that you are getting high-quality products that meet the necessary standards. Here’s a quick checklist to help you make an informed decision:
Check for Certifications: Look for TMT bars that are certified by recognized bodies like the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS). BIS certification guarantees that the product meets specific quality standards.
Verify Tensile Strength: Ensure that the TMT bars have the required tensile strength to withstand the loads imposed on your structure. Refer to the specifications provided by the manufacturer or consult with a structural engineer.
Inspect Ductility: Ductility is essential for TMT bars to absorb shock and prevent brittle failure. Check the ductility rating provided by the manufacturer.
Assess Corrosion Resistance: TMT bars should be resistant to corrosion to prevent structural degradation over time. Look for brands that offer corrosion-resistant coatings or treatments.
Compare Prices: Obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to compare prices and identify the best deals. However, don’t compromise on quality for the sake of cost.
Consider Brand Reputation: Choose a TMT bar brand with a good reputation in the industry. Look for brands that have a proven track record of providing reliable and high-quality products.
Verify Manufacturer’s Warranty: A warranty can provide peace of mind and protection against defects. Check if the manufacturer offers a warranty for their TMT bars.
Consult with Experts: If you are unsure about which TMT bars to choose, consult with a structural engineer or construction expert who can provide personalized advice based on your project requirements.
Read More: What is Commercial Construction? A Deep Dive
List of Top 5 Best TMT Bar in India for Construction
1. Tata TISCON
A well-established brand known for its high-strength, corrosion-resistant TMT bars. Tata Tiscon bars are manufactured using advanced technology and adhere to stringent quality standards.
2. SAIL TMT
SAIL, a government-owned steelmaking company, offers a range of TMT bars that are known for their reliability and durability. Their TMT bars are used in various construction projects across India.
3. JSW Steel
JSW Steel is another major player in the Indian steel industry, producing high-quality TMT bars. Their TMT bars are known for their excellent tensile strength and ductility.
4. Jindal Panther TMT Rebars
Jindal Panther TMT rebars are known for their high tensile strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance. They are manufactured using advanced technology and are widely used in various construction projects across India.
5. Kamdhenu TMT (Kamdhenu Nxt)
A leading private-sector steel company, Kamdhenu offers a wide range of TMT bars for different construction applications. Their TMT bars are known for their superior strength and earthquake resistance.
Read More: Understanding the Different Types of Tender in Construction
Prices for Best Steel for Construction
The prices of Steel TMT bars vary from state to state and brand to brand. On average, the prices of the best steel for construction range from ₹48 to ₹65 per kilogram. In tonnes, these prices would be ₹48,000 to ₹65,000.
Conclusion
Selecting the best steel for construction in India is crucial for ensuring the structural integrity, durability, and safety of any building project. The “best” brand of steel can vary depending on specific project requirements, such as load-bearing capacity, corrosion resistance, durability, budget, and aesthetic preferences. However, some well-regarded steel brands in India include Tata TISCON, SAIL TMT, JSW steel TMT, Jindal Panther Steel TMT, and Kamdhenu TMT.
What is Commercial Construction? A Deep Dive
Commercial construction often faces misconceptions, with many people assuming it’s just a larger version of residential building projects. However, a recent literature review highlighted the growing complexity and scale of commercial construction, revealing how these projects require specialized knowledge and advanced planning far beyond what most expect.
To clarify, commercial construction involves the design, renovation, and building of structures intended for business purposes, such as offices, retail spaces, or industrial facilities. This differs significantly from residential construction, which focuses solely on homes and apartments for private living.
In this blog, we will provide a comprehensive overview of commercial construction, exploring the unique aspects of this sector, its types, differences with residential construction and key trends shaping the industry today.
Read More: A Comprehensive Overview of Basic Building Components
Understanding Commercial Construction
Commercial construction refers to the building or renovation of structures that are used for business purposes. These can include office buildings, retail spaces, restaurants, cafes, hotels, educational buildings, sports complexes, etc.
Commercial construction projects often involve more complex planning, design, and engineering than residential construction, as they need to meet specific requirements for functionality, safety, and accessibility.
They also require coordination with various stakeholders, including architects, engineers, contractors, and property owners.
According to a report by Construction Week, the commercial real estate industry in India is expected to grow at a CAGR (Compound Annual Growth Rate) of approximately 13% during the period 2022- 2027.
Types of Commercial Construction
Commercial construction encompasses a wide range of building types, each with its own unique requirements and challenges. Here’s a breakdown of some of the most common types:
1. Office Buildings
Office buildings are perhaps the most common type of commercial construction. They can range from small, single-story structures to towering skyscrapers. Office buildings can further be classified into corporate offices, public sector offices, co-working spaces, and more.
2. Retail Spaces
Retail spaces can vary widely in size and scope, from small neighbourhood shops to large shopping malls. Office buildings can further be classified into shopping malls, strip centres, specialty stores and more.
3. Industrial Facilities
Industrial facilities are designed to support manufacturing, warehousing, and other industrial processes. They can range from small workshops to large-scale factories. Some common types include warehouses, factories, manufacturing plants and more.
4. Hospitality Venues
Hospitality venues provide lodging and other services to travellers. They can range from budget-friendly motels to luxury resorts. Some common types include hotels, resorts, motels, restaurants, B&B (Bed and Breakfast), and more.
5. Educational Institutions
Educational institutions provide educational services to students of all ages. They can range from small private schools to large public universities. Some common types include schools, universities, colleges, coaching centres and more.
6. Sports Complex
Sporting events are conducted within the sports complex. Some of the common types of sports complexes are stadiums, golf course, arena, racing tracks, inside game premises and more types of sports complexes for large and small spectator gatherings.
7. Medical Facilities
Medical facilities include hospitals, pharmacy, pathology lab, radiology lab, medical research centre, blood bank, etc. The facilities adhere to strict safety and health regulations.
Read More: How Construction ERP Software Unifies Your Business Operations
Commercial vs. Residential Construction: Key Differences
While both commercial and residential construction fall under the umbrella of private construction, they differ significantly in scale, financing, site size, and equipment requirements.
| Parameter | Commercial Construction | Residential Construction |
|---|---|---|
| Scale | Typically larger, involving multiple stories, larger buildings, or expansive complexes. | Smaller, typically focusing on single-family homes or small apartment complexes. |
| Financing | Funded by private investments, commercial loans, or a combination. Often attracts investors seeking long-term returns. | Funded by private investments and mortgages, often by individual homeowners or small-scale developers. |
| Site Size | Requires more extensive sites to accommodate large buildings, parking, and multiple structures. | Smaller, focused on individual homes or small complexes. |
| Equipment | Requires specialized equipment like cranes, heavy machinery, and advanced construction technology. | Generally requires less specialized equipment, with basic machinery suitable for small- to medium-scale projects. |
Read More: Understanding the Different Types of Tender in Construction
Levels of Commercial Construction
Commercial construction projects can range from small-scale renovations to massive, multi-year infrastructure projects. Here’s a breakdown of the different levels:
1. Small-Scale Construction
Scope: Typically involves minor renovations, repairs, or expansions.
Timeline: Relatively short, often completed within a few weeks or months.
Equipment: Requires less specialized equipment and a smaller workforce.
Examples:
. Installing new windows, doors, or roofing
. Interior office renovations
. HVAC system upgrades
2. Mid-Scale Construction
Scope: Involves more significant upgrades, expansions, or new construction.
Timeline: Longer than small-scale projects, often lasting several months or a year.
Equipment: Requires more specialized equipment and a larger workforce.
Examples:
. Building mid-size offices, hotels, or medical facilities.
. Constructing a new wing for an existing building
3. Large-Scale Construction
Scope: Involves major changes to the building footprint or the creation of entirely new structures.
Timeline: Extensive, often lasting several years.
Equipment: Requires highly specialized equipment and a large, coordinated team.
Examples:
. Building skyscrapers, shopping malls, or large office complexes
. Infrastructure projects like airports or bridges
Key Difference
| Feature | Small-Scale | Mid-Scale | Large-Scale |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scope | Minor | Significant | Major |
| Timeline | Short | Medium | Long |
| Equipment | Less Specialized | More Specialized | Highly Specialized |
| Workforce | Smaller | Larger | Very Large |
Read More: Top 10 Construction Companies in India
Conclusion
In conclusion, commercial construction encompasses a wide range of building projects, from towering office buildings to sprawling industrial facilities. This complex process involves a collaborative effort among developers, contractors, architects, engineers, and subcontractors, each playing a crucial role in delivering successful projects.
FAQs: Commercial Construction
What is commercial construction project management?
Commercial construction project management involves overseeing the planning, execution, and completion of commercial building projects, which can be done efficiently through a robust ERP Software for construction.
What is an example of a commercial construction project?
A perfect example of a commercial construction project is corporate offices. Other examples of commercial construction include shopping malls, hotels, restaurants, institutional buildings, etc.
What is the meaning of commercial building?
A commercial building is a structure designed and built for business purposes.
Choose the Right HIPAA Compliance Software for Hospitals
Shields Health Care Group, a Massachusetts-based medical imaging service provider, experienced a data breach in 2022 that exposed the personal information of over 2 million patients
This incident not only resulted in significant financial losses but also tarnished the organization’s reputation and eroded patient trust. The consequences of such breaches can be devastating, leading to identity theft, financial fraud, and even legal action.
This was just one of many data breaches reported annually.
To safeguard patient data and avoid the dire consequences of non-compliance, hospitals must prioritize HIPAA compliance.
This critical regulation mandates the implementation of robust security measures to protect sensitive patient information.
Specialized ERP solutions with HIPAA compliance software plays a pivotal role in achieving this goal, offering a comprehensive suite of tools and features designed to ensure data integrity and confidentiality.
In this blog, we will delve into the importance of HIPAA compliance for hospitals and explore how HIPAA compliance software can streamline the process of meeting regulatory requirements.
Understanding HIPAA Compliance: A Crucial Aspect of Hospital Management Software
HIPAA compliance is a critical factor to consider when selecting hospital management software. Healthcare providers can avoid HIPAA concerns by choosing a HIPAA-compliant hospital management software (HMIS).
What is HIPAA?
HIPAA stands for Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, a U.S. federal law enacted in 1996. HIPAA sets standards for the handling, storage, and transmission of EHR (Electronic Health Records) by healthcare providers. Non-compliance with HIPAA can lead to severe consequences.
Read More About HIPAA: HIPAA Compliance in India
Why is HIPAA Compliance Crucial for Hospitals?
Following HIPAA standards is completely optional in India because HIPAA is a US federal law that only applies to covered entities of the United States.
However, healthcare providers in India that handle US patient data or have business relationships with US entities may need to comply with HIPAA.
Healthcare providers have a responsibility to protect their patients’ sensitive health information. HIPAA compliance demonstrates a commitment to patient privacy and security.
Adhering to HIPAA compliance in India helps hospitals maintain credibility and stay competitive in the healthcare industry.
To mitigate the risks, hospitals must implement a robust HMIS solution that is HIPAA compliant, effective and up-to-date. This HMIS software can help hospitals:
- Encrypt patient data: Protecting it from unauthorized access.
- Monitor network activity: Identifying potential threats.
- Implement access controls: Restricting access to EHR to authorized personnel.
- Provide training: Educating employees about HIPAA regulations and best practices.
Read More: What is HMIS & Why Every Hospital Should Have An HMIS
How Our Software Ensures HIPAA Compliance
We’ve designed a comprehensive HMIS solution to meet the standards set by the HIPAA, providing you with the peace of mind that your patients’ data is protected.
Robust Security Features
Our software incorporates a suite of advanced security features to safeguard your patients’ information:
- Encryption: We employ strong encryption algorithms to protect data both in transit and at rest, preventing unauthorized access.
- Access Controls: Our granular access controls ensure that only authorized personnel can view and modify patient data, minimizing the risk of unauthorized disclosure.
- Regular Audits: We conduct regular audits to identify and address any potential vulnerabilities, ensuring that our security measures remain effective.
- Business Associate Agreements: We require all our business associates to comply with HIPAA regulations, ensuring that your patients’ data is protected throughout the entire healthcare ecosystem.
Comprehensive Data Privacy Measures
Our commitment to data privacy extends beyond security features. We implement robust data privacy measures to protect your patients’ information:
- Data Minimization: We collect and retain only the necessary data to provide our services, reducing the risk of unauthorized access or disclosure.
- Data Retention Policies: We adhere to strict data retention policies, ensuring that patient data is retained for the appropriate duration and then securely disposed of.
- Incident Response Plan: We have a comprehensive incident response plan in place to promptly address any security breaches and minimize their impact.
By choosing our HIPAA-compliant software, you can rest assured that your organization is meeting the highest standards of security and privacy. Our comprehensive approach to data protection ensures that your patients’ sensitive information is always safeguarded.
How HIPAA Compliance Software Can Help Hospitals
By choosing our HIPAA compliance software solution, you can enhance patient privacy, reduce the risk of data breaches, improve patient satisfaction, simplify compliance efforts, and gain a competitive advantage over competitors.
Patient privacy: Our HMIS solution ensures that sensitive patient information is protected from unauthorized access. With robust security features and encryption protocols, you can maintain the confidentiality of patient data and build trust with your patients.
Risk of data breaches: Data breaches can have devastating consequences for healthcare organizations, including financial losses, reputational damage, and legal penalties. Our HIPAA compliant software incorporates advanced security measures to minimize the likelihood of data breaches and protect your organization from costly incidents.
Patient satisfaction: Patients are increasingly concerned about the security of their personal health information. By choosing our HIPAA compliant software, you demonstrate your commitment to patient privacy and data protection. This can foster trust and confidence among patients, leading to increased satisfaction and loyalty.
Automated compliance tracking: Our software is designed to streamline compliance efforts and reduce the administrative burden on your staff. With built-in features and tools, you can easily manage compliance tasks and avoid penalties.
Competitive advantage: By ensuring safety, you can position your organization as a leader in patient privacy and data security. This can attract more patients, improve your reputation, and enhance your bottom line.
Read More: HIPAA Compliance Checklist: A Guide for Indian Healthcare Providers
Conclusion
In this blog, we have explored the critical importance of HIPAA compliance Software. We discussed the specific regulations outlined in the HIPAA Privacy Rule and Security Rule, emphasizing the need for robust security measures to protect Employee Health Records (EHR).
If your hospital is seeking a HIPAA compliance software solution that can streamline operations and ensure patient data security, we recommend you to contact us to learn more about our comprehensive hospital management software. Our platform is designed to meet the standards of HIPAA compliance, providing you with peace of mind and protecting your patients’ sensitive information.
Request a demo today to see how our HIPAA Compliance software can benefit your hospital.
What is POS Software and How Does It Work
POS software has become an essential tool for modern businesses, streamlining operations and providing valuable insights. It serves as the central hub for managing transactions, inventory, customer data, and more. Additionally, it offers a range of benefits that improve efficiency, accuracy, and customer satisfaction.
By understanding the significance and capabilities of POS software, businesses can make informed decisions to optimize their operations and drive growth.
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of POS software, exploring its components, functionalities, and the process of selecting the right system for your business.
What is a Point of Sale (POS) Software?
POS software is a computerized application designed to streamline and manage sales transactions in retail, hospitality, and other businesses. It handles sales transactions, invkentory management, customer data, and more. Think of it as the backbone of your business operations, facilitating seamless interactions between customers and your staff.
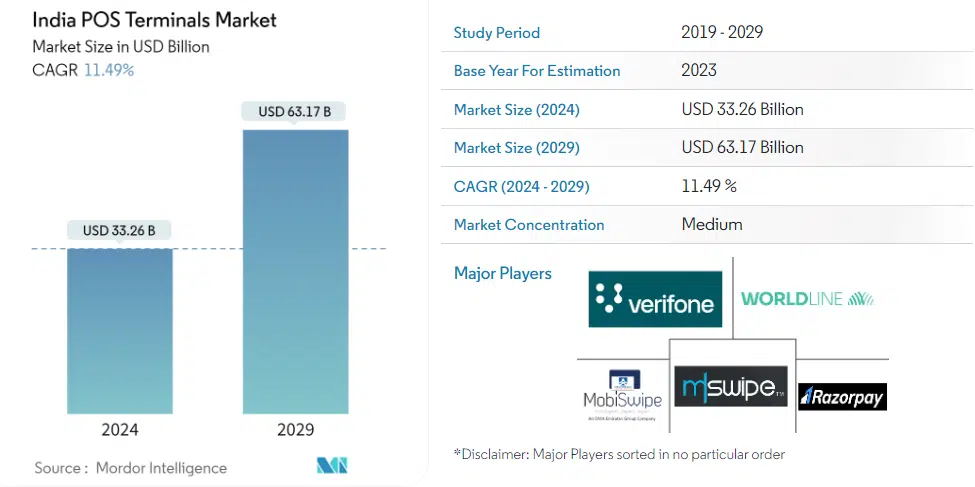
According to Mordor Intelligence, the India market size of POS terminals is estimated at USD 33.26 billion in 2024, and it is expected to reach USD 63.17 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 11.49%.
Read More: Impact of GST on Hotel Industry
Components of a POS System
A typical POS system comprises two primary components: hardware and software.
Hardware components may include:
Barcode scanners: These devices read product barcodes, capturing essential information like product ID, price, and quantity.
Receipt printers: They generate printed receipts for customers, detailing the items purchased and the total amount due.
Cash drawers: These secure compartments store cash and other payments received.
Touchscreen terminals: These provide a user-friendly interface for cashiers to input sales data and manage transactions.
Payment terminals: These devices accept various payment methods, including credit cards, debit cards, and mobile payments.
Software components typically include:
Sales module: This handles the recording of sales transactions, including item selection, quantity, pricing, and payment processing.
Inventory management module: This tracks product stock levels, monitors inventory costs, and helps prevent stock outs or overstocking.
Customer management module: This stores customer information, purchase history, and preferences, enabling personalized marketing and loyalty programs.
Reporting module: This generates various reports, such as sales summaries, inventory reports, and employee performance metrics.
Integration capabilities: This allows the POS system to connect with other business systems like accounting software, CRM platforms, and e-commerce solutions.
Common POS System Features
POS systems offer a wide range of features to cater to the specific needs of different businesses. Some of the most common features include:
Inventory management: Track stock levels, manage purchase orders, and prevent stockouts.
Sales tracking: Analyze sales data to identify trends, monitor performance, and make data-driven decisions.
Customer management: Collect customer information, personalize interactions, and implement loyalty programs.
Employee management: Assign permissions, track employee performance, and manage time and attendance.
Payment processing: Accept various payment methods, including credit cards, debit cards, and mobile payments.
Reporting: Generate customizable reports to gain insights into business performance.
Integration capabilities: Connect with other business systems for seamless data flow.
How Does POS Software Work?
A POS system operates as a centralized hub for managing sales transactions. It streamlines the entire process, from capturing customer orders to processing payments and generating reports.
Step-by-Step Process of a Transaction
1. Customer Interaction: The customer presents their desired items to the cashier.
2. Item Scanning: The cashier scans each item’s barcode using a barcode scanner. The POS system retrieves the corresponding product information, including price and quantity.
3. Price lookup: The POS system retrieves the product’s price and other relevant information from its database.
4. Order Review: The POS displays the customer’s order, allowing the cashier to review and make any necessary adjustments.
5. Payment Processing: The customer chooses their preferred payment method (e.g., cash, card, digital wallet). The POS system processes the payment and generates a receipt.
6. Transaction Completion: Once the payment is successful, the POS system updates inventory levels, records the sale in the sales history, and generates a customer receipt.
7. Total calculation: The system calculates the total price based on the quantity and price of each item.
8. Receipt generation: The POS system prints a receipt detailing the items purchased, total amount, and payment information.
Role of Barcode Scanners and RFID Technology
Barcode Scanners: These devices read the unique barcode on each product. The barcode contains information such as the product’s SKU, price, and description.
RFID Technology: Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) tags can be attached to products or used in conjunction with barcode scanners. RFID technology enables faster and more accurate item tracking, especially for bulk items or items with multiple SKUs.
Integration with Other Business Systems
POS software often integrates with other business systems to create a cohesive and efficient workflow. Common integrations include:
Inventory Management: POS systems can automatically update inventory levels as items are sold, ensuring accurate stock counts and preventing stockouts.
Accounting Software: POS data can be seamlessly transferred to accounting systems for financial reporting, tax calculations, and reconciliation.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Customer information captured in the POS system can be synchronized with CRM software to track customer preferences, purchase history, and loyalty programs.
Loyalty Programs: POS systems can integrate with loyalty programs to track customer points, rewards, and promotions.
E-commerce Platforms: For businesses with both physical and online stores, POS systems can integrate with e-commerce platforms to synchronize inventory, pricing, and customer data.
Types of POS Software
POS software comes in various forms to suit different business needs and preferences. Some common types include:
Cloud-based POS systems: These systems are hosted on remote servers, allowing businesses to access them from anywhere with an internet connection. They offer scalability, ease of use, and regular updates.
On-premises POS systems: These systems are installed on-site within the business premises. They provide greater control over data security and customization but may require more upfront investment and maintenance.
Mobile POS systems: These systems are designed to be used on mobile devices like smartphones or tablets. They are ideal for businesses that need to process sales on the go, such as food trucks or pop-up shops.
Specialized POS systems: These systems are tailored to specific industries, such as retail, hospitality, or healthcare. They offer industry-specific features and functionalities.
Choosing the Right POS Software
Selecting the appropriate POS software for your business involves careful consideration of several factors:
Business size and needs: Assess your current and future business requirements to determine the necessary features and functionalities.
Budget: Consider your budget constraints and the long-term costs associated with hardware, software, and maintenance.
Scalability: Choose a system that can grow with your business and accommodate future expansion.
Integration capabilities: Ensure the POS system can integrate with other business systems you use, such as accounting software or CRM platforms.
Ease of use: Look for a system with a user-friendly interface that is easy for your staff to learn and operate.
Customer support: Evaluate the level of customer support provided by the vendor, including response times and availability of resources.
Aatithya POS is a comprehensive solution designed to meet the diverse needs of businesses, from small retail stores to large restaurant chains. With its robust features, seamless integration, and scalable architecture, Aatithya can help businesses streamline operations, improve efficiency, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Read More: Night Audit: Steps in Night Audit process in Front Office
Conclusion
A POS software system is a valuable asset for businesses of all sizes, providing efficiency, accuracy, and insights into sales performance. By understanding the components, features, and types of POS software, you can make an informed decision and select a system that aligns with your business goals.
We encourage you to explore the various POS software options available and consider contacting us for a demo or more information. Our team of experts can help you find the ideal solution to optimize your business operations and drive growth.
A Comprehensive Overview of Basic Building Components
A building is a well-connected combination of several structural components, known as building components. Some components are basic building components without which the hypothesis of building is baseless.
Every component of a building has its own purpose and requirement to support the building structure. The inclusion or exclusion of the structural components is decided based on the type of the building and region where it is being built.
The choice of components, their location, and their contribution to the structural integrity of a building are determined by architects and structural designers.
Some of the basic components of building include foundation, roof, plinth, plinth beam, walls, window, doors, etc.
While the exact number of building components can vary as per the user requirement, here are some basic components of building structure:
Read Also: Top 5 Best Cement in India & Their Prices
Key Components of a Building Structure
These are necessary components of a building structure, generally they are three in number:
1. Substructure
2. Plinth
3. Superstructure
1. Substructure
The substructure, or foundation, is arguably the most critical component of any building structure. It’s the invisible part of a building, lying below the ground level that supports the entire weight of the building and transfers it to the underlying soil.
A well-designed and constructed foundation ensures the building’s stability, durability, and resistance to external forces like earthquakes and wind.
According to the National Concrete Association (NCA), foundations typically account for 10-15% of the total cost of a building.
Common foundation types include:
Shallow foundations:
. Spread footings: Individual concrete pads supporting columns or walls.
. Combined footings: Multiple columns supported by a single, larger footing.
. Mat foundations: A continuous slab of concrete covering the entire building area.
Deep foundations:
. Pile foundations: Cylindrical elements driven or drilled into the ground to transfer loads to deeper, stronger soil layers.
. Caissons: Hollow shafts drilled into the ground and filled with concrete to provide support.
The choice of foundation type depends on several factors, including:
Soil conditions: The bearing capacity of the soil determines the foundation’s depth and design.
Building load: The weight of the building, including materials, occupants, and equipment, influences the foundation’s size and strength.
Seismic activity: In regions prone to earthquakes, foundations must be designed to withstand lateral forces.
Water table: The level of groundwater can impact foundation design to prevent moisture-related issues.
2. Plinth and Plinth Level
A plinth, often overlooked but crucial, serves as the connecting link between a building’s superstructure and substructure. It’s also an invisible building component below or equal to the ground level.
It’s essentially a raised platform, providing a stable base for visible building components like walls, window, door, roof, another floor, etc.
Types of Plinths:
Brick Plinth: A common and cost-effective option, brick plinths are constructed using bricks and mortar.
Concrete Plinth: Offering superior strength and durability, concrete plinths are often preferred for larger or heavier buildings.
Stone Plinth: A traditional and visually appealing choice, stone plinths can add a touch of elegance to a building.
Key Functions of a Plinth:
Structural Support: Plinths distribute the weight of the building evenly across the foundation, preventing uneven settlement and potential structural damage.
Protection from Moisture: They act as a barrier against rising damp, protecting the building’s walls and interior from moisture-related issues.
Aesthetic Appeal: Plinths can enhance the visual appearance of a building, adding a finished look and elevating its overall aesthetic.
3. Superstructure
The superstructure is the portion of a building that stands above ground level. It’s the part you see and interact with most directly. While the foundation provides the base, the superstructure is the building’s functional and aesthetic heart.
Key Components of the Superstructure:
- Walls: These are the vertical elements that enclose the building’s interior space. They can be load-bearing, supporting the roof and floors, or non-load-bearing, simply providing enclosure.
- Floors: These horizontal elements divide the building into levels. They can be made of various materials like concrete, wood, or steel.
- Roof: The uppermost part of the building, the roof protects the interior from the elements. It can be flat, sloped, or gabled, and its design depends on factors such as climate and architectural style.
- Windows and Doors: These openings in the walls allow for natural light, ventilation, and access to the building.
The Role of Superstructure in Building Function
The superstructure plays a crucial role in determining a building’s functionality:
- Structural Support: The walls, floors, and roof must be designed to withstand the weight of the building and any additional loads, such as snow, wind, or seismic activity.
- Thermal Comfort: The materials used in the superstructure, along with insulation and ventilation systems, influence the building’s energy efficiency and internal temperature.
- Aesthetics: The appearance of the superstructure, including its materials, colors, and architectural details, contributes to the overall visual appeal of the building.
Read Also: Top 10 Construction Companies in India
A Breakdown of Building Components
Basically, the other building components are sub-part of the superstructure of the building, which are as follows:
1. Floor
The floor is a horizontal building component constructed atop the plinth level. It provides a solid base for the building’s interior and can be made from various materials, including concrete, marble, granite, and more. Prior to floor installation, the ground must be thoroughly compacted and levelled to ensure a stable and even floor.
2. Walls
Walls are the vertical structures that define a building’s boundaries and provide essential support. Unlike columns, which are typically slender, walls are thicker and more substantial. Their primary function of walls is to assist columns in carrying the weight of the building’s floors and roof and transferring these loads to the foundation/substructure below.
Walls can be constructed from various materials, including bricks, stones, concrete blocks, and more. Bricks come in many types, such as AAC blocks, burnt clay bricks, CLC blocks, hollow concrete blocks, and solid concrete blocks. The choice of material depends on factors like cost, durability, and insulation requirements.
Beyond their structural role, walls serve as a protective barrier against the elements. They shield the building’s interior from wind, rain, sunlight, and other external influences. Walls also create enclosed spaces within the building, providing privacy and defining different areas. To allow for ventilation, natural light, and access, walls are typically equipped with windows and doors.
3. Parapet
Parapets are protective wall structures typically built by extending the walls above horizontal roof slabs. They serve as a safety barrier, preventing people from falling off the roof. Parapet walls are generally 0.8 to 1.2 meters high, providing a sufficient height for protection without obstructing views or hindering access to the roof.
4. Columns
Columns are essential building components that provide crucial structural support. They extend from the foundation to the uppermost levels, transmitting loads from slabs to the ground. These vertical elements are typically constructed using concrete, but can also be made from materials like stone, brick, or metal.
There are two primary types of columns: structural and architectural. Structural columns prioritize load-bearing capacity, resisting forces from above and transferring them to the foundation. Architectural columns, on the other hand, are designed primarily for aesthetic purposes, enhancing the visual appeal of a building.
Columns can be cast into various shapes, including rectangular, circular, square, hexagonal, and more, offering flexibility in design and style.
Read Also: Understanding the Different Types of Tender in Construction
5. Sill
Sills are the horizontal bottom level of a window. It serves a crucial function in building structure. They protect the wall below from weathering and wear, while also providing a practical surface for the window frame to rest upon.
In architectural drawings, the top view or plan is often drawn at the level of the window sill. This perspective provides a clear understanding of the window’s placement in relation to other building components.
The choice of material for window sills depends on factors such as the building’s overall style, budget, and the specific requirements of the window. Common materials include stone, metal, and wood.
6. Lintels
Lintels are horizontal structural components of building that span over openings in walls, such as doorways or windows. These building components are crucial for supporting the weight of the structure above the opening and preventing it from collapsing.
Common Materials and Construction Methods:
- Reinforced Concrete: This is the most common material for lintels due to its strength, durability, and versatility. Reinforced concrete lintels are typically cast in place or prefabricated.
- Steel: Steel lintels are often used in commercial and industrial buildings, especially where large spans are required. They can be hot-rolled or fabricated.
- Wood: While less common in India today, wooden lintels were once widely used in residential construction.
Traditional Methods and Modern Alternatives:
- Brick or Stone Lintels: Historically, lintels were often constructed using bricks or stones. However, these materials are generally not suitable for modern construction due to their limited load-bearing capacity and susceptibility to weathering.
- Modern Alternatives: Modern construction techniques often employ prefabricated concrete lintels or engineered steel beams, which offer superior strength, durability, and efficiency.
7. Beams
Slender, elongated basic components of building, the beams are designed to carry loads and transmit them to supporting columns or walls. They are typically positioned beneath slabs to provide structural support.
8. Slab
These are flat, plate-like building structures that provide horizontal support and separate different floors within a building. The topmost slab, often referred to as the roof slab, serves as the protective covering for the entire building structure.
A slab is a horizontal structural component that serves both as a floor and a ceiling in a building. Its primary function is to distribute and transfer loads from above to the supporting structural elements, such as walls and columns.
- In a single-story building: The slab typically forms the roof, providing a weather-resistant cover and supporting the building’s external cladding.
- In multi-story buildings: Slabs act as the ceiling of one floor and the floor of the floor above. This layered arrangement allows for efficient load transfer and creates distinct levels within the structure.
9. Staircase
Stairs are an essential building component in multi-story buildings, providing a means for residents to navigate between floors and transport materials. Designed in various shapes and sizes to accommodate different spaces and loads, stairs are typically constructed within stairwells.
Stairwell Placement and Construction Materials
Stairwells are often positioned centrally or at the corners of buildings. They can be built using a range of materials, including concrete, metal, or timber.
Common Stair Types
A variety of stair configurations are available to suit different architectural structures and functional needs. Common types of stair include:
- Circular: Featuring a curved, continuous set of steps.
- Helix: Similar to circular stairs but with a spiral pattern.
- Dog-legged: Characterized by two parallel flights of stairs connected by a landing.
- Semi-circular: Half-circle stairs, often found in limited spaces.
- Square: Stairs with a square footprint.
- Double helix: Two spiral staircases intertwined.
- Rectangular: Straight, rectangular stairs.
10. DPC (Damp Proof Course)
DPC, or Damp Proof Course, is a waterproofing barrier typically applied at the base of walls, especially in basements, to prevent moisture from rising through the masonry and causing dampness or damage. This layer acts as a shield, blocking the upward movement of water and ensuring a healthier and more durable structure.
11. Roof
The roof is a critical component of any building, serving as its protective covering. Its design and construction vary widely depending on factors such as climate, architectural style, and building function.
The roof’s material and design can affect the building’s energy consumption and durability.
Roof Structure:
The roof is typically composed of:
- Roof Covering: This is the outer layer that protects the building from the elements. It can be made of materials such as shingles, tiles, metal sheets, or even green vegetation (in green roofs).
- Roof Deck: The structural layer beneath the covering, providing support and distributing loads. It can be made of concrete, metal or wood.
- Rafters or Trusses: These are the structural components that support the roof deck and transfer loads to the building’s walls or columns.
Read More: How Construction ERP Software Unifies Your Business Operations
Wrapping Up
In conclusion, understanding the various building components and their interactions with other basic components of building is essential for architects, engineers, and construction professionals. By carefully considering factors such as materials, design, and load-bearing capacity, it is possible to create building structures that are both durable and sustainable.
HIPAA Compliance Checklist: A Guide for Indian Healthcare Providers
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) was enacted in 1996 to safeguard the privacy and security of patient’s health records(EHR). It established a set of national standards for the protection of EHR to ensure that individuals have control over their personal health data. HIPAA is a crucial component of the healthcare landscape, as it helps to maintain patient trust, prevent data breaches, and comply with legal requirements.
However, adhering to HIPAA compliance can be a complex and daunting task for healthcare organizations. They must choose a solution that is capable enough to navigate a labyrinth of regulations, implement robust security measures, and train their staff to handle EHR appropriately. The challenges faced by healthcare organizations include:
- Data breaches
- Complex regulations
- Limited resources
- Rapidly evolving technology
Read More: Top 5 Hospital Management Software in India
HIPAA Compliance Checklist
The following checklist outlines the key areas that software development companies must address:
Risk Assessment
- Conduct a thorough risk assessment to identify potential vulnerabilities in your systems and EHR.
- Prioritize risks based on their likelihood and impact.
- Develop a plan to mitigate identified risks and vulnerabilities.
Security Policies and Procedures
Implement robust security measures to protect patient data, such as:
- Access controls: Restrict access to patient information based on roles and responsibilities.
- Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data both at rest and in transit.
- Physical security: Protect physical facilities and equipment from unauthorized access.
Technical Controls
- Implement firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption.
- Keep all software and hardware components up-to-date with the latest security patches and updates.
Physical Security
- Implement physical safeguards to protect EHR from unauthorized access, theft, or loss. This may involve using locked storage facilities, access controls, and surveillance systems.
- Restrict access to EHR on a need-to-know basis. Only authorized personnel should have access to sensitive patient information.
Business Associate Agreements
- If you work with business associates who handle patient data, ensure that they have appropriate safeguards in place.
- Establish Business Associate Agreements (BAAs) that outline the responsibilities and obligations of both parties.
Incident Response Plan
Create a detailed incident response plan to address security breaches effectively. This should include steps for identifying, containing, and remediating incidents, as well as notifying affected individuals and regulatory authorities.
Monitoring and Auditing
- Regularly monitor compliance: Conduct ongoing monitoring activities to ensure that your software and processes are in compliance with HIPAA. This may involve reviewing access logs, auditing systems, and conducting security assessments.
- Conduct audits to identify gaps: Periodically conduct audits to identify any gaps in your compliance program. This can help you to address issues proactively and maintain a high level of security.
Read More: Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM): A Quick Guide
Empowering HIPAA Compliance with Our Hospital Management Software (HMIS)
At Aarogya, we understand the critical importance of HIPAA compliance for healthcare organizations. Our hospital management software is meticulously designed to provide a robust and comprehensive solution that safeguards patient health information and streamlines compliance efforts.
Key Features for HIPAA Compliance:
- Robust Access Controls: Granular access controls are implemented through our software solution to ensure that only authorized personnel can access EHR. This helps to prevent unauthorized disclosure and protect patient privacy.
- Advanced Encryption: We employ state-of-the-art encryption algorithms to safeguard EHR both at rest and in transit. This protects against unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Audit Trails: Our software maintains detailed audit trails, tracking all user activities and system events. This enables organizations to monitor compliance, identify potential vulnerabilities, and respond to incidents promptly.
- Risk Assessment Tools: Aarogya incorporates tools to help healthcare organizations conduct regular risk assessments and identify potential threats to EHR. This proactive approach allows for timely mitigation of risks and prevention of breaches.
- Business Associate Management: We provide features to manage business associate agreements (BAAs) effectively. Our software ensures that all business associates comply with HIPAA requirements, reducing the risk of data breaches.
- Incident Response Planning: The software system includes templates and tools to help healthcare organizations develop comprehensive incident response plans. This ensures that they are prepared to respond effectively to security breaches and minimize their impact.
- Employee Training: Integrated training modules are provided by software and our team to help healthcare organizations educate their staff on HIPAA compliance. This ensures that employees are aware of their responsibilities and can handle EHR appropriately.
How Our Software Simplifies HIPAA Compliance
- Centralized Management: Our software provides a centralized platform for managing HIPAA compliance efforts. This simplifies the process, reduces administrative burden, and ensures consistency across the organization.
- Automation: Our software automates many of the routine tasks associated with HIPAA compliance, such as risk assessments, audit reviews, and reporting. This frees up valuable time for healthcare professionals to focus on patient care.
- Continuous Monitoring: Our software provides real-time monitoring of compliance activities, allowing organizations to identify and address potential issues promptly. This helps to prevent breaches and maintain compliance.
- Expert Support: We in-house a team of more than 30 experts to provide guidance and support throughout the HIPAA compliance journey. We can help organizations navigate complex regulations, implement best practices, and address any challenges they may encounter.
Read More: WhatsApp Automation for Hospitals
Conclusion: HIPAA Compliance Checklist
In conclusion, HIPAA compliance checklist is a critical responsibility for software development companies that work with healthcare organizations. By following the key components of the Security and Privacy Rules, implementing robust security measures, and training staff on HIPAA requirements, companies can protect EHR and avoid costly penalties.
By partnering with Aarogya, healthcare organizations can confidently navigate the complex landscape of HIPAA regulations and focus on providing high-quality patient care.
HIPAA Compliance in India: Protecting Patient Data and Ensuring Security
HIPAA Compliance in India: When we think about data security, it’s not limited to social media or servers of large organizations.
Data security is imperative, especially in the healthcare industry.
In an era where electronic health records (EHRs) are increasingly prevalent, even the Government of India is also promoting digital healthcare through the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission, safeguarding patient information has become more critical than ever.
A breach of patient data can lead to serious consequences, including identity theft, financial loss, and damage to the reputation of HMIS providers.
To address these concerns, industry standards and regulations have been established to ensure the protection of sensitive health information.
HIPAA compliance in India is one such crucial standard that healthcare organizations must adhere to.
For healthcare providers in India, understanding and implementing HIPAA compliance is essential to safeguard patient data and maintain trust.
Understanding HIPAA
HIPAA stands for Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act. It is a federal law in the United States that sets standards for the privacy and security of personal health information (PHI).
HIPAA sets forth a set of rules and guidelines to protect the privacy and security of patient’s health information. At the same time, it lets doctors and hospitals use this information to treat patients, bill for services, and run their healthcare businesses.
Generally, HMIS solution providers offer the capability to store and easily access patient information. To ensure data security and compliance with HIPAA regulations, it’s essential to select a reliable HMIS provider for your healthcare facility.
Key Components of HIPAA
1. Privacy Rule: This rule establishes standards for the use and disclosure of PHI by healthcare facilities. It protects individuals’ rights to access, amend, and receive a copy of their PHI.
2. Security Rule: This rule sets standards for the security of electronic PHI. It requires healthcare facilities to implement administrative, technical, and physical safeguards to protect PHI from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, or modification.
3. Breach Notification Rule: This rule requires healthcare facilities to notify individuals and the top government regulatory authority in the event of a data breach that compromises PHI.
Read More: What is HMIS & Why Every Hospital Should Have An HMIS
HIPAA Compliance in India
Adhering to HIPAA compliance standards can pose unique challenges for Indian healthcare services providers. Some of the key challenges include:
Cultural and Linguistic Barriers: Communicating complex HIPAA regulations to healthcare professionals who may not be fluent in English can be difficult.
Technological Limitations: Many healthcare facilities in India may lack the necessary infrastructure or resources to implement robust security measures.
Limited Awareness: There may be a lack of awareness about HIPAA compliance among healthcare professionals and administrators.
Cost Implications: Implementing HIPAA compliance measures can be costly, particularly for smaller healthcare facilities.
Despite these challenges, HIPAA compliance also presents significant opportunities for Indian healthcare providers. By demonstrating their commitment to data privacy and security, healthcare facilities can:
Enhance Patient Trust: Patients are increasingly concerned about the security of their personal health information. By complying with HIPAA, healthcare providers can build trust with patients.
Improve Reputation: HIPAA compliance can enhance the reputation of healthcare facilities, attracting more patients and business partners.
Stay Competitive: As healthcare becomes increasingly globalized, HIPAA compliance can give Indian healthcare providers a competitive advantage.
What Does It Mean to Be HIPAA-Compliant in India?
A HIPAA-compliant HMIS provider is committed to safeguarding the privacy and security of its clients’ sensitive health information (PHI). This commitment involves a comprehensive approach that includes:
- Robust Technical Safeguards: Implementing strong security measures to protect PHI from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, or alteration.
- Data Integrity and Availability: Ensuring that PHI is accurate, complete, and accessible when needed.
- Employee Training: Educating staff on HIPAA regulations and best practices for handling PHI to prevent breaches.
- Vendor Management: Requiring associated third-party vendors to adhere to HIPAA standards and conducting due diligence to ensure compliance.
- Regular Audits and Assessments: Conducting periodic reviews of data security practices to identify and address potential vulnerabilities.
Our HIPAA Compliance HMIS Solution for India's Healthcare Sector
Aarogya is one of the leading hospital management information System (HMIS) solution providers in India, serving a wide range of healthcare organizations, including clinics, hospitals, laboratories, pharmaceutical, telemedicine providers, health technology firms, insurance companies, blood banks, research institutions, government agencies, and academic medical centers.
How Aarogya Stays Updated of HIPAA Compliance
At Aarogya HMIS, we’re committed to ensuring our clients can confidently utilize their data. To achieve this, we stay meticulously updated on the latest HIPAA regulations and requirements. Here’s how we keep our team informed:
- Monitoring HHS Updates: As the primary enforcer of HIPAA, we closely follow the Department of Health and Human Services’ website for regular updates and guidance.
- Attending Industry Events: Our leadership team regularly participates in industry conferences and training sessions to stay abreast of the latest HIPAA developments and compliance best practices.
- Subscribing to Industry Publications: We subscribe to leading publications to stay informed about changes in HIPAA regulations, their impact on data ecosystems, and innovative compliance solutions.
- Conducting Regular Internal Audits: To ensure our team’s ongoing adherence to HIPAA, we conduct frequent quality audits to identify and address any compliance gaps.
Read More: Top 5 Hospital Management Software in India
Conclusion
In conclusion, HIPAA compliance in India is a crucial aspect of healthcare data management. By adhering to the principles outlined in HIPAA, healthcare providers can safeguard patient information, maintain trust, and avoid costly penalties.
What is Cloud Kitchen? A Guide for Restaurant Owners
What is Cloud Kitchen: Nowadays, businesses are preferring to open and run cloud kitchens instead of traditional dine-in restaurants.
This shift can be attributed to the numerous advantages offered by cloud kitchens and the evolving preferences of consumers.
In India, the concept of cloud kitchen came into existence after immense popularity of the food delivery aggregators like Zomato and Swiggy.
Almost all of the business of cloud kitchens rely on food delivery aggregators.
Consumers increasingly rely on food delivery aggregators to enjoy delicious meals without leaving the comfort of their homes or offices.
The convenience and variety offered by food delivery platforms has also reduced the burden of restaurants.
According to IMARC Group, the Indian cloud kitchen market is poised to experience significant growth, expanding from $969.5 million in 2023 to $2,948 million by 2032 at a CAGR of 13.2%.
In this blog, we will discuss about What is Cloud Kitchen, it’s advantages and how it is different from traditional restaurants.
What is Cloud Kitchen
A cloud kitchen is a commercial kitchen space that is designed specifically for food delivery and takeout orders.
Unlike traditional restaurants with physical dining areas, cloud kitchens focus solely on preparing and delivering food.
This eliminates the need for a physical store for customer dine-in. This innovative approach offers numerous advantages for both restaurateurs and consumers alike.
Cloud kitchens rely solely on food delivery aggregator platforms to reach their customers.
These kitchens are typically located in shared commercial spaces, allowing multiple businesses to operate under one roof while sharing costs like rent, utilities, and equipment.
Read More: Steps in Night Audit process in Front Office
Cloud Kitchen Vs Ghost Kitchen
Cloud kitchen, dark kitchen, virtual kitchen, shadow kitchen, ghost kitchen, commissary kitchen are the same. Fundamentally, such restaurants specializes in fulfilling digital orders.
While the terms “cloud kitchen” and “ghost kitchen” are the same and often used interchangeably, there are subtle distinctions between the two.
| Feature | Cloud Kitchen | Ghost Kitchen |
| Branding | Can be branded or unbranded | Branded |
| Concept | Multiple Concepts | Single Concept |
| Physical Presence | May or may not have physical store | Typically, no physical store |
Cloud Kitchen Vs Traditional Restaurants
Cloud kitchens are becoming a popular alternative to traditional brick-and-mortar restaurants. While both models have their own advantages, understanding the key differences between them will give you a clearer picture of the industry.
| Feature | Traditional Restaurants | Cloud Kitchen |
| Physical Presence | Yes. Dine-In experience. | No. Only Delivery & Takeaways. |
| Operational Costs | Higher operational cost | Lower operational costs |
| Menu Flexibility | fixed menu to cater to a diverse customer base | more niche or limited-time menus for specific customer base. |
| Scalability | Expansion can be capital-intensive and time-consuming | Offer greater scalability, allowing businesses to easily expand. |
| Manpower | Large Staff Requirements with Teams | Less Staffing Requirements |
Types of Cloud Kitchen
After discussing What is Cloud Kitchen, lets see the different types of cloud kitchens.
1. Brand-Owned Cloud Kitchen:
This is the most traditional and widely adopted model. A single restaurant brand owns and operates the cloud kitchen, preparing food exclusively under its own name. While offering complete control over the brand, this model requires significant investment in marketing and customer acquisition.
2. Multi-Brand Kitchen/Shared Space:
In a multi-brand kitchen, multiple restaurants or brands share a common kitchen space. This shared model is a cost-effective option for businesses looking to reduce operational expenses, especially those starting out.
3. Commissary Kitchen:
Many food delivery aggregators have launched their own commissary kitchens, offering empty kitchen spaces and minimal infrastructure for rent. Restaurants can utilize these fully equipped or partially equipped kitchens on a shared basis. This model allows multiple small kitchens to operate within a larger space, with various restaurant brands cooking simultaneously.
4. Outsourced Kitchen:
In an outsourced kitchen model, a third-party provider manages most of the critical kitchen operations. This allows business owners to focus on food preparation, menu development, and marketing, while outsourcing infrastructure and logistics-related tasks to external professionals.
Read More: Impact of GST on Hotel Industry
Benefits of Cloud Kitchen

Minimal Initial Investment
Cloud kitchen concept doesn’t require much space, even it could be run from the comfort of your home. Therefore, the initial setup cost as compared to restaurants is very less. Further, it could be started within a few days or weeks.
Lower Overhead Cost
Cloud kitchens do not have the burden of expensive utilities, high property tax, rent of the space, salaries to high number of employees and maintenance cost. They may share communal expenses with other tenants.
Enhanced Convenience
Virtual kitchen providers often take care of tasks like health inspections, equipment repairs, janitorial services, security monitoring, property taxes, and utility bills. By freeing up your time from these responsibilities, you can invest more energy into perfecting your menu and delivering exceptional customer service.
Minimal Delivery Errors
Cloud kitchens provide the infrastructure to facilitate deliveries from a single location, boosting your revenue. By utilizing both a traditional restaurant and a cloud kitchen, you can handle increased demand without compromising the quality of service.
Meeting Evolving Customer Demands
As the demand for convenient and affordable food delivery continues to surge, cloud kitchens play a pivotal role in meeting these expectations. By optimizing delivery processes, reducing costs, and embracing technological advancements, cloud kitchens ensure a seamless and efficient experience for customers.
Experimentation and Innovation
Cloud kitchens offer a unique opportunity for restauranteurs to experiment with new concepts and ideas without the high risks associated with traditional brick-and-mortar establishments.
Expanding Brand Reach
Cloud kitchens provide a strategic platform for businesses to expand their reach and attract new customers. By focusing on food delivery, restaurants can tap into a vast market and leverage popular delivery apps like Zomato, Swiggy and social media channels. This broader marketing approach helps to increase brand visibility and drive customer acquisition.
Read More: What is KOT | Importance of KOT in Hotel Industry | KOT Full Form
Choosing the right ERP for Your Cloud Kitchen
After understanding What is cloud Kitchen, its types, working, let’s see how to manage it through tools like ERP.
ERP software solutions like Aatithya is the backbone of cloud kitchens, streamlining operations from order intake to delivery.
Almost all of the orders are placed online through the restaurant’s website, app, or delivery aggregators. This makes the robust ERP software system indispensable.
A cloud kitchen requires an integrated Restaurant management software that seamlessly handles online orders, payments, and kitchen management.
A crucial component is a point of sale (POS) system capable of accepting orders from various channels, including delivery aggregators and your own online platforms.
The software solution provides valuable insights into sales data, allowing you to track performance across different channels and make data-driven decisions.
While partnering with food aggregators is essential, building your own restaurant website or mobile app can offer an additional sales channel and enhance customer loyalty.
Effective inventory management is another critical aspect of cloud kitchen operations.
ERP software solutions can track stock consumption, trigger timely reorders, and help reduce wastage.
This ensures that food costs are controlled and operations run smoothly.
By investing in the right restaurant management software, you can streamline your cloud kitchen operations, improve efficiency, and deliver exceptional customer experiences.
Book a free online Demo of Aatithya Restaurant Management software today to explore how our integrated technology solution can benefit your cloud kitchen.
Conclusion- What is Cloud Kitchen
Cloud kitchens offer several advantages over traditional restaurants, including cost-effectiveness, operational efficiency, and flexibility. However, they also present unique challenges, such as intense online competition and reliance on delivery platforms.
Despite these challenges, cloud kitchens provide exciting opportunities for food entrepreneurs. To succeed in this competitive market, effective management and the right tools are crucial. A robust restaurant management software can significantly streamline operations, improve inventory management, and optimize procurement processes, ultimately contributing to the success of your cloud kitchen business.
So, we have discussed what is cloud kitchen in this blog in detail, Share your thoughts, if any, in the comments below.
FAQs
What does cloud kitchen do?
Cloud kitchen is a concept specifically designed for food delivery and takeout orders.
Is Zomato a cloud kitchen?
No, Zomato is not a cloud kitchen. It is a food delivery aggregator.
Is Swiggy a cloud kitchen?
No, Swiggy is not a cloud kitchen. It is a food delivery aggregator.
Can I start a cloud kitchen from home?
Yes, Off-course. Cloud kitchens can be operated from your own home or rented home. You will need to prepare food as per the order in your kitchen and give it to the delivery partners.
How to start a cloud kitchen?
To start a cloud kitchen, you need to pick a name for your kitchen and FSSAI, GST and other licences. Then, register yourself in food aggregator platforms like Zomato and Swiggy. After successful onboarding, you will start getting orders, prepare food and deliver it to delivery partners.